Flowchart ประกอบด้วย 3 รูปแบบคือ
1.แบบ Sequence
2.แบบ Decision
3.แบบ Loop หรือ Iteration
1. ผังงานตามลำดับ Flowchart(Sequence)
รูปแบบการเขียนโปรแกรมที่ง่ายที่สุดคือ เขียนให้ทำงานจากบนลงล่าง เขียนคำสั่งเป็นบรรทัด และทำทีละบรรทัดจากบรรทัดบนสุดลงไปจนถึงบรรทัดล่างสุด สมมติให้มีการทำงาน 3 กระบวนการคือ อ่านข้อมูล คำนวณ และพิมพ์The flowchart above demonstrates a sequence of steps. The reader would start at the Start shape and follow the arrows from one rectangle to the other, finishing at the End shape. A sequence is the simplest flowcharting construction. You do each step in order.
If your charts are all sequences, then you probably don't need to draw a flowchart. You can type a simple list using your word processor.

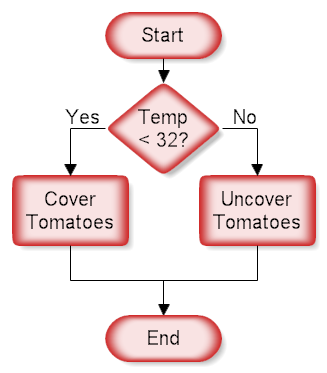
2.ผังงานแบบทางเลือก Flowchart(Decision)
การตัดสินใจ หรือเลือกเงื่อนไขคือ เขียนโปรแกรมเพื่อนำค่าไปเลือกกระทำ โดยปกติจะมีเหตุการณ์ให้ทำ 2 กระบวนการ คือเงื่อนไขเป็นจริงจะกระทำกระบวนการหนึ่ง และเป็นเท็จจะกระทำอีกกระบวนการหนึ่ง แต่ถ้าซับซ้อนมากขึ้น จะต้องใช้เงื่อนไขหลายชั้น เช่นการตัดเกรดนักศึกษา เป็นต้น ตัวอย่างผังงานนี้ จะแสดงผลการเลือกอย่างง่าย เพื่อกระทำกระบวนการเพียงกระบวนการเดียวThis structure is called a decision, "If Then.. Else" or a conditional. A question is asked in the decision shape. Depending on the answer the control follows either of two paths.
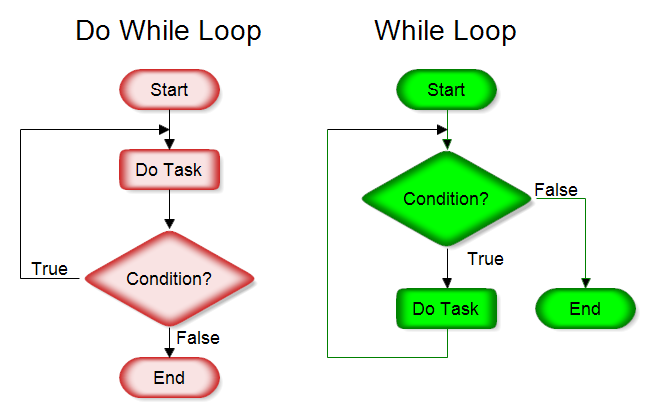
3.ผังงานแบบวนซ้ำ Flowchart(Loop/Iteration)
การทำกระบวนการหนึ่งหลายครั้ง โดยมีเงื่อนไขในการควบคุม หมายถึงการทำซ้ำเป็นหลักการที่ทำความเข้าใจได้ยากกว่า 2 รูปแบบแรก เพราะการเขียนโปรแกรมแต่ละภาษา จะไม่แสดงภาพอย่างชัดเจนเหมือนการเขียนผังงาน ผู้เขียนโปรแกรมต้องจินตนาการด้วยตนเองThis structure allows you to repeat a task over and over. The red chart above on the left does the task and repeats doing the task until the condition is true. The green chart on the right checks the condition first and does the task while the condition is true. It is not important that you remember whether the loop is a "Do While" or "Repeat Until" loop, only that you can check the condition at the start of the loop or at the end. You can also have the conditions reversed and your loop is still a structured design loop. A slight variation of the above is the "For each...do the following" loop shown below.
No comments:
Post a Comment